







Question 1: What is the battery used for?
The battery is no stranger to those who drive frequently. Most models can see their position directly when they open the engine compartment cover. The batteries of individual models will also be placed in the trunk. Its main function is to provide the required power to the starter when the vehicle starts, and to provide power for the interior electrical appliances such as sound system, lighting system, etc. when the engine is insufficient or not activated, and when the engine starts to supply normally, the battery will Collect and store electrical energy for future use.
Question 2: How to look at the battery parameters?
   When we buy or observe a battery, we can always see a lot of parameters, which represent the performance and specifications of the battery. There are three main parameters related to our daily car. The first is the capacity, the unit is Ah (Ah), and 1Ah represents the discharge of 1 amp for 1 hour. The higher the value, the greater the capacity of the battery and the greater the ability to store electrical energy. The second is the voltage in V (volts). Represents the operating voltage of the battery, usually the vehicle battery voltage (cold car voltage) is 12V. The third is the current, the unit is A (A), which is mainly related to the starting performance. The labeling of this parameter is different for different batteries. Some batteries directly indicate the cold start current CCA value at a specific temperature, such as 430CCA, which means that the battery has a cold start current of about 430A at a specific temperature (usually -18 °C).
Question 3: How many batteries are there?
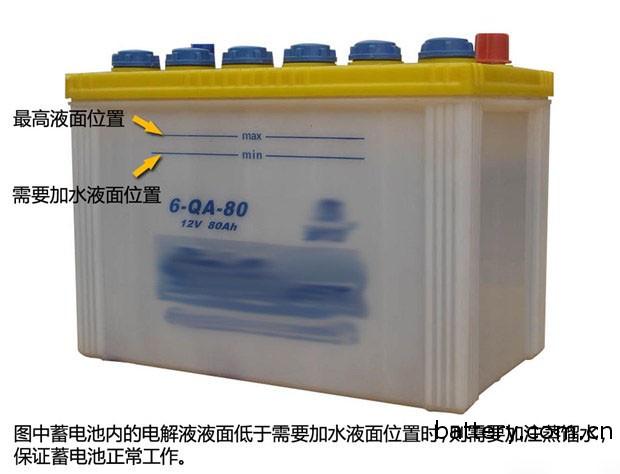
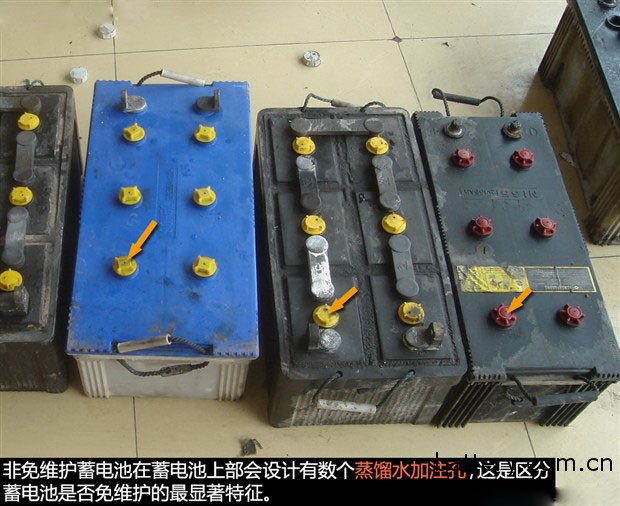
   Generally speaking, the batteries that we usually use are mainly divided into three types: ordinary batteries, dry batteries and maintenance-free batteries. Among them, ordinary batteries and dry batteries are collectively referred to as non-maintenance batteries, so we can also simply divide them into non-maintenance-free and maintenance-free. The method of distinguishing between the two batteries is also very simple. If you have distilled water filling holes on the upper surface of your battery, then you are using a non-maintenance battery, and maintenance-free batteries do not have this design. On non-maintenance batteries, there is usually a liquid level indication, such as a tick mark. When the warning position is lower than the warning position, distilled water is added to ensure normal operation of the battery. From the point of view of use, maintenance-free batteries are more convenient, but the price is relatively high.
Question 4: What is inside the battery?
   After introducing the classification of the battery, you must have a preliminary understanding of the battery used in your car. Why can the battery supply power to the vehicle? Where does this power come from? To understand this, we must start with its structure.
   The batteries commonly used in our cars are called lead-acid batteries. In terms of composition, it is mainly composed of an oxide of lead, lead and an aqueous solution of sulfuric acid, wherein the oxides of lead and lead are the main raw materials for the storage components of the battery, and are responsible for storing the electrical energy in the battery, while the aqueous solution of sulfuric acid is the battery. The electrolyte mainly provides a medium for charging and discharging the battery.
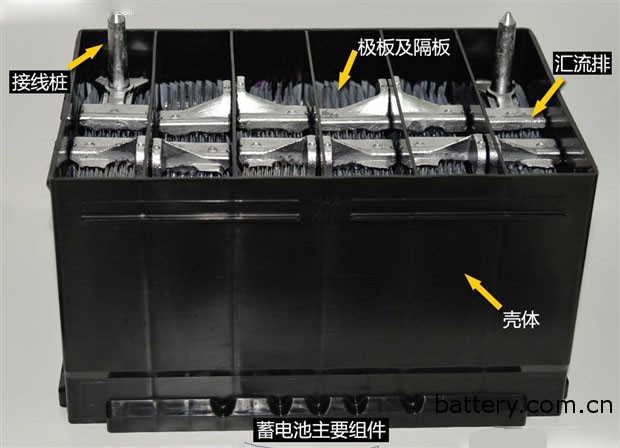
   From the perspective of battery structure, commonly used lead-acid batteries can be mainly divided into positive plate, negative plate, separator, bus bar, housing, electrolyte, wiring pile and other components. The positive and negative plates are mainly composed of lead, which is responsible for storing the electric energy in the battery. For the same battery, the number of positive and negative plates determines the size of the battery, and the more the number of plates, the larger the battery capacity. The separator is made of an insulating porous material, mainly for preventing short-circuiting of the positive and negative electrodes, and helps to prevent the surface active material from falling off and adsorbing and storing a certain amount of electrolyte. The electrolyte is the medium for the transfer of active substances between the positive and negative electrodes of the battery, and is the environmental basis for charging and discharging the battery. The function of the bus bar is to connect the various plate sets in series, which is equivalent to the internal wires of the battery. The terminal block is the part that is connected to the body circuit and is equivalent to the power socket. Needless to say, the role of the housing is mainly responsible for storing the battery components and the electrolyte.
   The charging and discharging process of the battery mainly relies on its own internal chemical reaction to convert chemical energy into electrical energy. This process is relatively complicated and has little to do with our daily use of the car, so there is no need to elaborate on the detailed principle. Here is just a brief description of what happens to the battery during charging and discharging. When the battery is discharged, the sulfuric acid in the electrolyte will continue to decrease, and the water will gradually increase; the charging process is just the opposite, the water in the electrolyte will continue to decrease, and the sulfuric acid will increase. At the end of charging, water will decompose into hydrogen and oxygen gas, which will make the water in the battery less and less, which is why non-maintenance batteries need to add distilled water from time to time.
Question 5: Are all the requirements for batteries the same?
   In addition to the different types of storage batteries in the structure, different models will have different requirements for the use of batteries. For example, with the start-stop function, when the start-stop system works frequently, the battery's power will drop rapidly, and the battery will always be in a deep discharge state, especially in the congested road section, so it has a start-stop function. The model requires a battery with a strong deep discharge capability.
   At present, for such batteries, AGM ultra-fine glass fiber separator (hereinafter referred to as AGM) is one of the main technical means of application. Compared with the traditional battery separator, the separator has the characteristics of stronger acid resistance, higher liquid absorption rate and smaller electric resistance, which can prolong the service life of the battery, and its maximum characteristic is that the deep discharge performance is good. Therefore, our common models with start-stop function basically use batteries with AGM partitions. For example, according to the person in charge of the Valta battery, if the brand battery label of the original car is marked with the AGM microfiber separator technology, then the car must have the start and stop function.
Question 6: Is there a difference in the manufacturing process of different batteries?
   Of course, in the field of battery technology, not only the separator technology is developing, but also the main energy storage component of the battery, the pole plate, is constantly changing. Especially the positive electrode plate with relatively strong energy storage capacity is regarded as the main process improvement. Object. As the core component of the battery, the plate not only determines the capacity of the battery, but also the life of the entire battery. At present, the battery plates sold in the market can be mainly divided into three types: casting plate, drawing plate and double-volt plate (the patented technology of Valta battery is currently used). The main difference between the three plates is the difference in manufacturing methods, and this difference also leads to a different battery life.
Question 7: How is the battery produced?
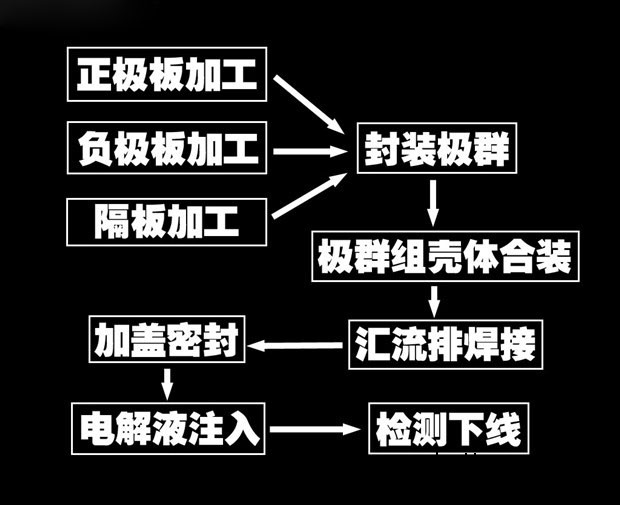
   So how is the battery produced? In fact, the manufacturing process of the battery is not long, and it can be divided into four major steps. First, the positive and negative plates are processed and transported to the package line by the positive and negative plate production lines. Subsequently, a spacer is added and packaged between the positive and negative plates on the package line, which is called an encapsulation pole group in the industry. In the third step, a plurality of packaged pole groups are assembled into a battery case, and the bus bar is welded to make the connection between the pole groups conductive. Finally, the battery is capped, sealed and added to the electrolyte. After these four steps, the battery has completed all the manufacturing processes, and can be packaged and sold after being tested.
Editor's summary:
   Whether the car can start normally is inseparable from the function of the battery. With the development of technology and technology, modern storage batteries have greatly improved their life expectancy and ease of use. With the start-stop technology and the gradual popularization of electric vehicles in the future, the battery is bound to continue to evolve. However, as far as the current market is concerned, the most important thing for ordinary car owners is whether they can launch the vehicle stably and reliably. A kind of technology battery, to meet the actual needs of users to the utmost, is definitely ranked first.